背景
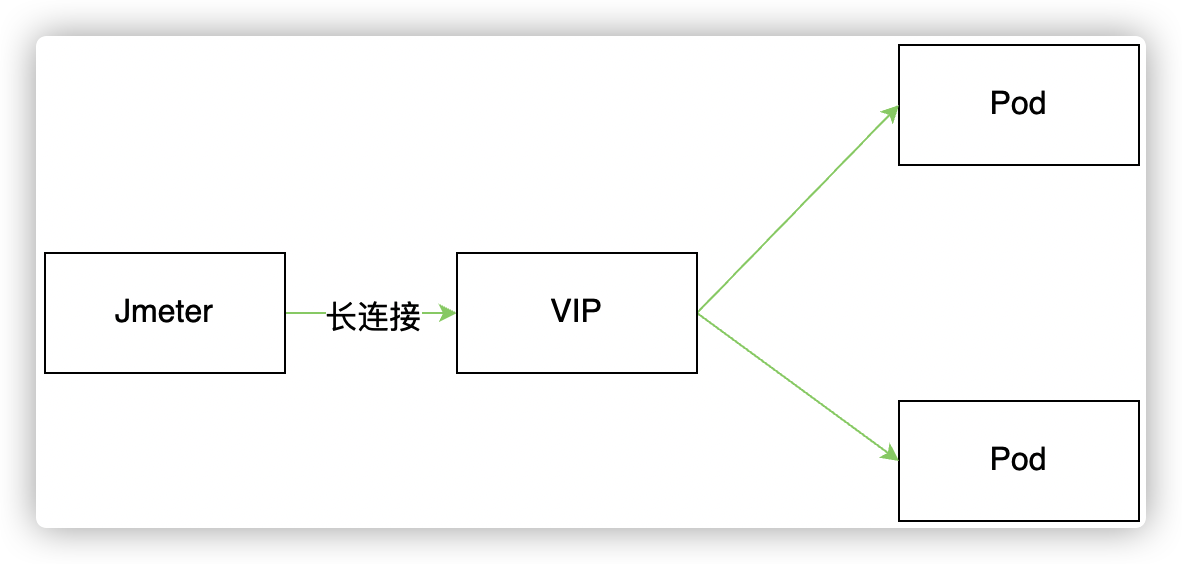
最近业务应用使用 Service ip 进行压测时,当容器销毁时,部分请求会出现 connect refused 错误。按照文档 云上 pod 下线引起短时服务不可用 进行优雅下线优化后有一定改善,但是仍然存在 connect refused 异常。本文通过分析 kube-router 实现 vip 的逻辑,进行定位问题根因,并举一反三对 kubernetes 默认组件 kube-proxy service IP 实现进行研究和分析。
IPVS VIP 实现
ipvs (IP Virtual Server) 是工作在内核态的4层负载均衡,也就是我们常说的4层LAN交换,作为 Linux 内核的一部分。ipvs运行在主机上,在真实服务器集群前充当负载均衡器。ipvs可以将基于TCP和UDP的服务请求转发到真实服务器上,从而达到通过单个 VIP 代理多个后端真实服务的目的。IPVS 和 iptables 一样都是基于内核底层 netfilter 实现,netfilter 主要通过各个链的钩子实现包处理和转发。
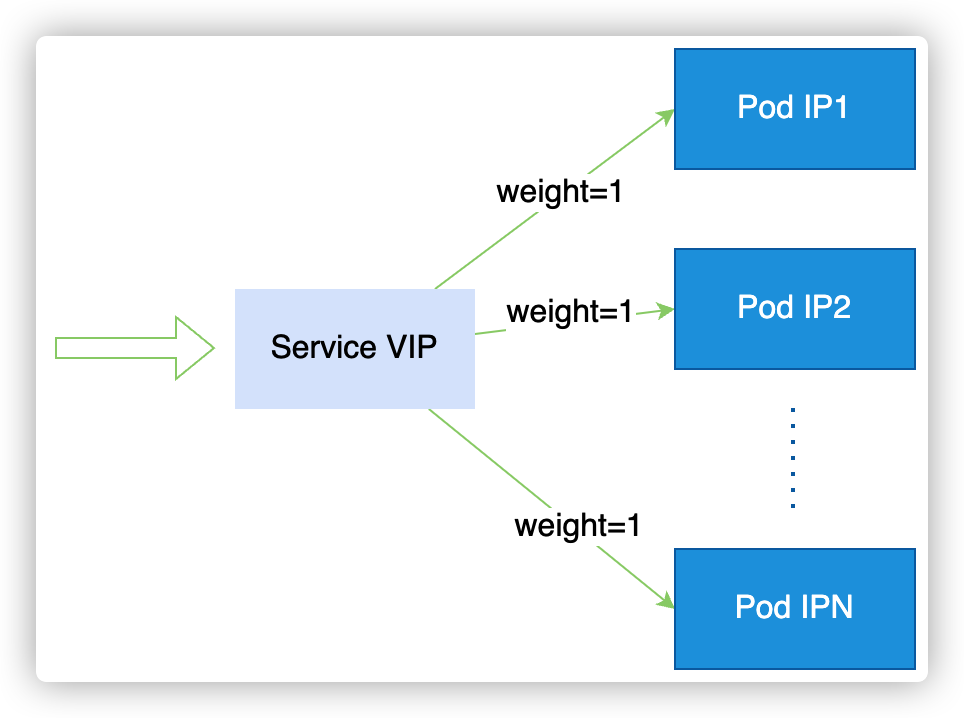
ipvs 作为内核中负载均衡,有多种负载策略:rr(轮询)、wrr(加权轮询)、sh(源地址哈希)等,默认使用 rr 模式。vip 后面关联多个 pod ip, 通过 VIP 请求后 ipvs 会根据配置的均衡策略选取其中一个 pod ip 进行流量转发。
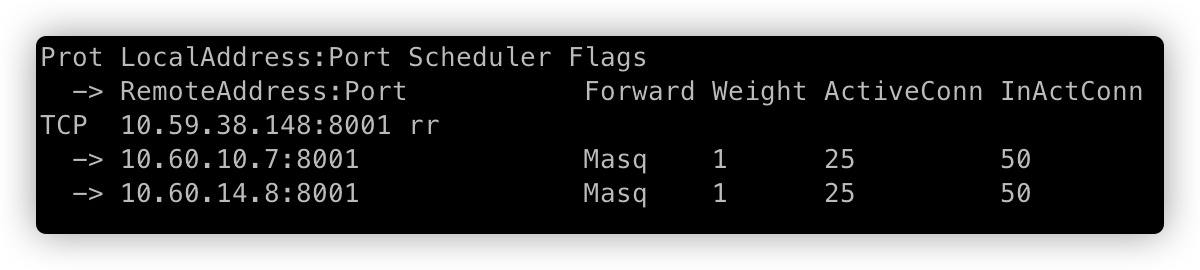
如上图,使用 ipvsadm 工具查看 10.59.38.148:8001 转发的 RS(Real Server) 有两个:10.60.10.7、10.60.14.8,转发策略为 RR,其中 Weight 标识每个 RS 的权重。
当 Weight=0 时,新连接不会转发到该 RS;但是,已建立的连接仍会保持,直到连接释放。ActiveConn 是活动连接数,也就是 tcp 连接状态的 ESTABLISHED;InActConn 是指除了 ESTABLISHED 以外的,所有的其它状态的 tcp 连接。
常用开源组件实现逻辑
kube-router
先已公司使用 cni 插件为 kube-router 作为研究对象,通过使用部署一个简单的 go http server 两副本应用,观察删除一个 Pod 后,会发生哪些变化:
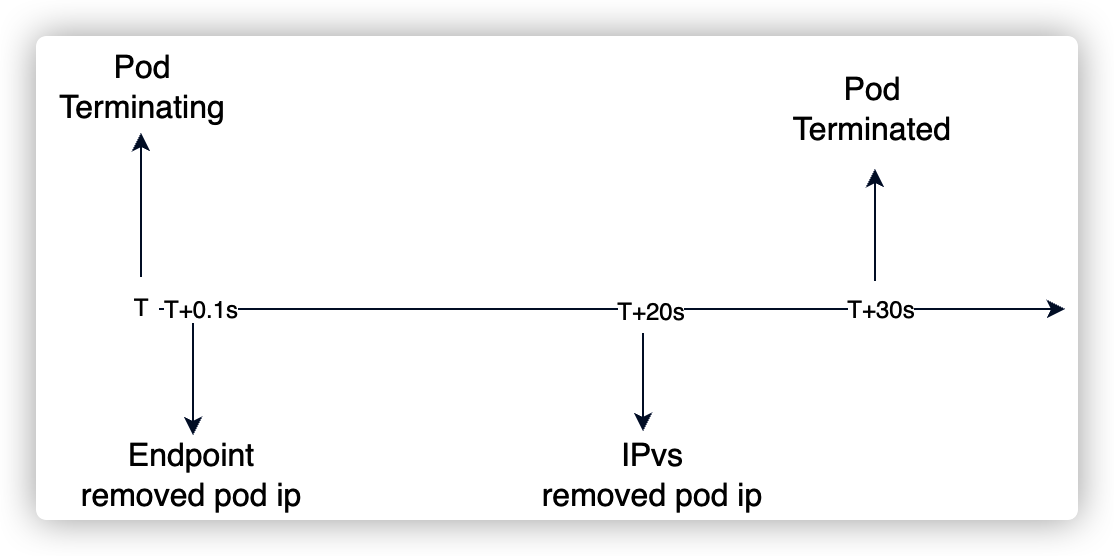
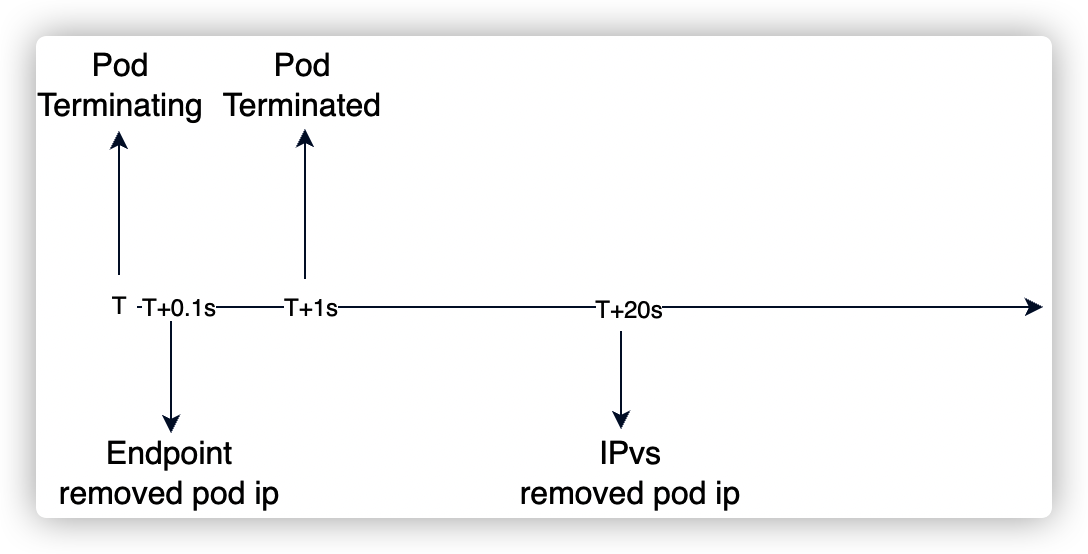
上面两张图,分别对应 http server 在是否处理 SIGTERM 信号场景下对 ipvs 更新的影响。
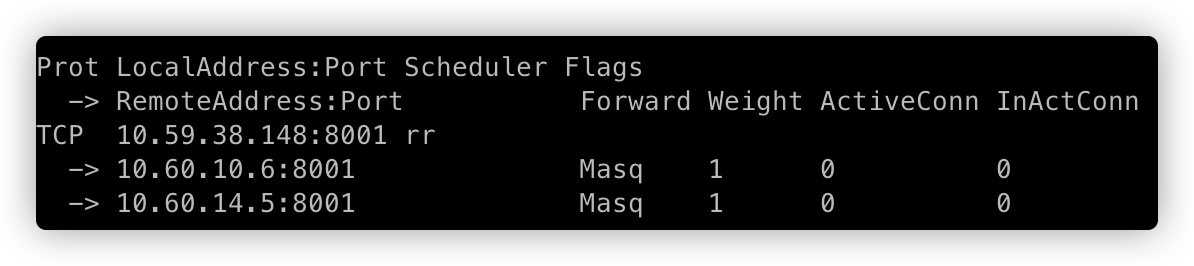
上图可以,看出当删除 Pod 时,在 20s+ 以后 kube-router 才会将被删除的 pod IP 在 ipvs 中摘掉。而摘掉流量方式是直接在 ipvs 中删除对应的 RS (10.60.10.7):
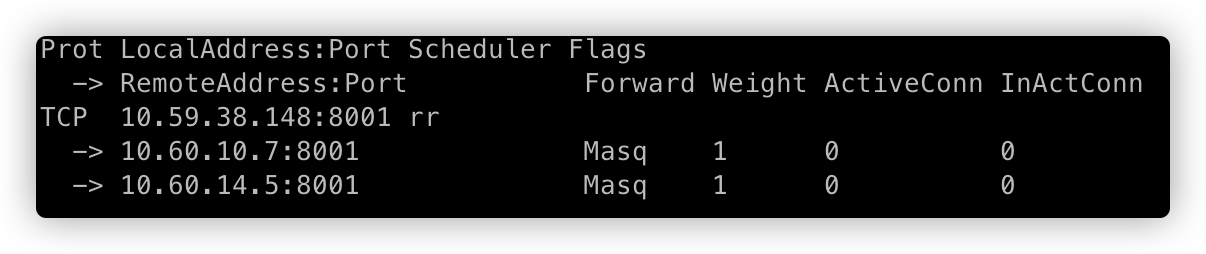 ==》
==》
这样,在两种场景下会出现异常:
- pod 容器已完全删除,但是 ipvs 还会转发流量到被删除的 Pod IP 上。也就容器完全删除早于 ipvs 中 RS 的删除动作;
- Ipvs 摘掉pod 流量时,存在未释放的连接。也就是 ipvs 中 RS 删除早于 pod 销毁,并且存在持久化的会话;
第一种问题还是未做好优雅下线导致的,可以通过 prestop 来增加优雅下线,提前将连接释放掉。但是,由于删除后 20s 仍然又新连接进来,虽然解决了第一个场景问题,但是第二个场景问题还是会存在的。
在上述业务压测出现问题的场景中:
- 业务容器已经做了优雅下线(等待15s+业务层开始优雅下线逻辑),整个优雅下线时间>=15s;
- 修改业务容器 terminatedGracePeriod 时长为 120s 后,我们抓包发现没有新流量进入,但仍然存在 connect refused 异常;
出现问题场景,属于第二种。那第二种问题如何解决呢?回答这个问题前,先要弄清楚下面疑问:
- 首先,为什么 ipvs 在 20s 后才会将 pod ip 摘掉;
- 之前有了解过 ipvs 中 RS weight=0 时,新流量不会转发到该 RS,那 kube-router 有没有实现这个逻辑呢?
带着上面两个问题,我们来看一下 kube-router 源码。
源码分析
kube-router 内部会通过 list/watch 来监听 endpoint 和 service 更新,当 endpoint 发生变更(pod 删除)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| // proxy/network_services_controller.go
func (nsc *NetworkServicesController) OnEndpointsUpdate(ep *api.Endpoints) {
... ...
// build new service and endpoints map to reflect the change
newServiceMap := nsc.buildServicesInfo()
newEndpointsMap := nsc.buildEndpointsInfo()
if len(newEndpointsMap) != len(nsc.endpointsMap) || !reflect.DeepEqual(newEndpointsMap, nsc.endpointsMap) {
nsc.endpointsMap = newEndpointsMap
nsc.serviceMap = newServiceMap
glog.V(1).Infof("Syncing IPVS services sync for update to endpoint: %s/%s", ep.Namespace, ep.Name)
nsc.sync(synctypeIpvs)
} else {
glog.V(1).Infof("Skipping IPVS services sync on endpoint: %s/%s update as nothing changed", ep.Namespace, ep.Name)
}
}
// OnServiceUpdate handle change in service update from the API server
func (nsc *NetworkServicesController) OnServiceUpdate(svc *api.Service) {
... ...
// build new service and endpoints map to reflect the change
newServiceMap := nsc.buildServicesInfo()
newEndpointsMap := nsc.buildEndpointsInfo()
if len(newServiceMap) != len(nsc.serviceMap) || !reflect.DeepEqual(newServiceMap, nsc.serviceMap) {
nsc.endpointsMap = newEndpointsMap
nsc.serviceMap = newServiceMap
glog.V(1).Infof("Syncing IPVS services sync on update to service: %s/%s", svc.Namespace, svc.Name)
nsc.sync(synctypeIpvs)
} else {
glog.V(1).Infof("Skipping syncing IPVS services for update to service: %s/%s as nothing changed", svc.Namespace, svc.Name)
}
}
|
可以看到 endpoint 和 service 更新,都是先更新 nsc 的 endpointMap 和 serviceMap,然后执行 nsc.sync 函数。nsc.sync 函数将变更类型同步到 syncChan:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| //proxy/network_services_controller.go
func (nsc *NetworkServicesController) sync(syncType int) {
select {
case nsc.syncChan <- syncType:
default:
glog.V(2).Infof("Already pending sync, dropping request for type %d", syncType)
}
}
|
syncChan 在 NetworkServiceController 的 Run 函数中进行监听:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
| // Run periodically sync ipvs configuration to reflect desired state of services and endpoints
func (nsc *NetworkServicesController) Run(healthChan chan<- *healthcheck.ControllerHeartbeat, stopCh <-chan struct{}, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
......
select {
case <-stopCh:
glog.Info("Shutting down network services controller")
return
default:
// kube-router 默认启动时,先更新一遍 ipvs
err := nsc.doSync()
if err != nil {
glog.Fatalf("Failed to perform initial full sync %s", err.Error())
}
nsc.readyForUpdates = true
}
// loop forever until notified to stop on stopCh
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
nsc.mu.Lock()
nsc.readyForUpdates = false
nsc.mu.Unlock()
glog.Info("Shutting down network services controller")
return
case <-gracefulTicker.C:
if nsc.readyForUpdates && nsc.gracefulTermination {
glog.V(3).Info("Performing periodic graceful destination cleanup")
nsc.gracefulSync()
}
// 从 syncChan 唤醒协程执行 ipvs 的更新/同步逻辑
case perform := <-nsc.syncChan:
healthcheck.SendHeartBeat(healthChan, "NSC")
switch perform {
case synctypeAll:
glog.V(1).Info("Performing requested full sync of services")
err := nsc.doSync()
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Error during full sync in network service controller. Error: " + err.Error())
}
case synctypeIpvs:
glog.V(1).Info("Performing requested sync of ipvs services")
nsc.mu.Lock()
// ipvs 的更新/同步逻辑
err := nsc.syncIpvsServices(nsc.serviceMap, nsc.endpointsMap)
nsc.mu.Unlock()
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Error during ipvs sync in network service controller. Error: " + err.Error())
}
}
if err == nil {
healthcheck.SendHeartBeat(healthChan, "NSC")
}
case <-t.C:
glog.V(1).Info("Performing periodic sync of ipvs services")
healthcheck.SendHeartBeat(healthChan, "NSC")
err := nsc.doSync()
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Error during periodic ipvs sync in network service controller. Error: " + err.Error())
glog.Errorf("Skipping sending heartbeat from network service controller as periodic sync failed.")
} else {
healthcheck.SendHeartBeat(healthChan, "NSC")
}
}
}
}
|
更新 ipvs 函数 nsc.syncIpvsServices :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| // proxy/service_endpoints_sync.go
// sync the ipvs service and server details configured to reflect the desired state of Kubernetes services
// and endpoints as learned from services and endpoints information from the api server
func (nsc *NetworkServicesController) syncIpvsServices(serviceInfoMap serviceInfoMap, endpointsInfoMap endpointsInfoMap) error {
start := time.Now()
defer func() {
endTime := time.Since(start)
if nsc.MetricsEnabled {
metrics.ControllerIpvsServicesSyncTime.Observe(endTime.Seconds())
}
glog.V(1).Infof("sync ipvs services took %v", endTime)
}()
var err error
var syncErrors bool
// map to track all active IPVS services and servers that are setup during sync of
// cluster IP, nodeport and external IP services
activeServiceEndpointMap := make(map[string][]string)
// 配置 VIP ipvs
err = nsc.setupClusterIPServices(serviceInfoMap, endpointsInfoMap, activeServiceEndpointMap)
if err != nil {
syncErrors = true
glog.Errorf("Error setting up IPVS services for service cluster IP's: %s", err.Error())
}
// 配置 nodeport ipvs
err = nsc.setupNodePortServices(serviceInfoMap, endpointsInfoMap, activeServiceEndpointMap)
if err != nil {
syncErrors = true
glog.Errorf("Error setting up IPVS services for service nodeport's: %s", err.Error())
}
err = nsc.setupExternalIPServices(serviceInfoMap, endpointsInfoMap, activeServiceEndpointMap)
if err != nil {
syncErrors = true
glog.Errorf("Error setting up IPVS services for service external IP's and load balancer IP's: %s", err.Error())
}
// 清理过期 vip
err = nsc.cleanupStaleVIPs(activeServiceEndpointMap)
if err != nil {
syncErrors = true
glog.Errorf("Error cleaning up stale VIP's configured on the dummy interface: %s", err.Error())
}
// 清理过期 RS IP
err = nsc.cleanupStaleIPVSConfig(activeServiceEndpointMap)
if err != nil {
syncErrors = true
glog.Errorf("Error cleaning up stale IPVS services and servers: %s", err.Error())
}
err = nsc.syncIpvsFirewall()
if err != nil {
syncErrors = true
glog.Errorf("Error syncing ipvs svc iptables rules to permit traffic to service VIP's: %s", err.Error())
}
err = nsc.setupForDSR(serviceInfoMap)
if err != nil {
syncErrors = true
glog.Errorf("Error setting up necessary policy based routing configuration needed for direct server return: %s", err.Error())
}
if syncErrors {
glog.V(1).Info("One or more errors encountered during sync of IPVS services and servers to desired state")
} else {
glog.V(1).Info("IPVS servers and services are synced to desired state")
}
return nil
}
|
每次有 endpoint/service 发生变化,nsc.syncIpvsServices 都会将所有ipvs 更新一遍,整个函数执行时间根据 service 数量不同执行时间不同。在我们线下环境有 3200 个 service,函数执行时间 30s+。
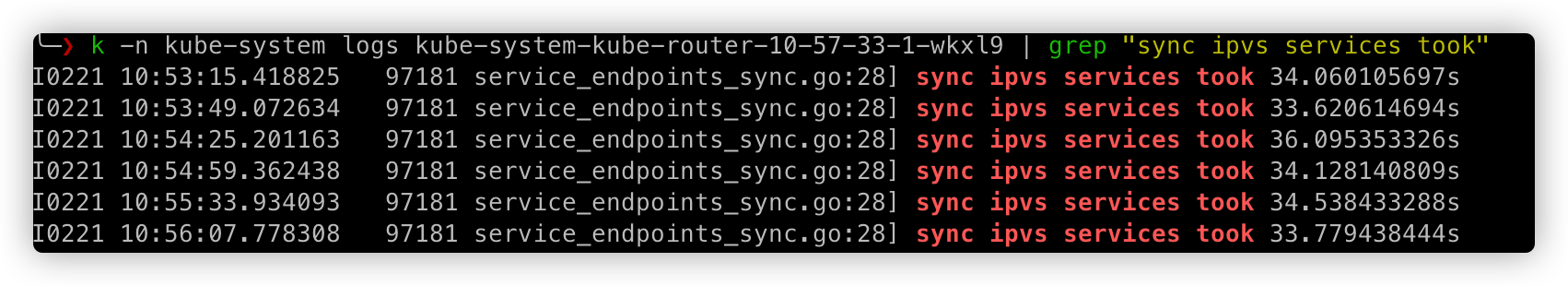
这就解答了「为什么 ipvs 在 20s 后才会将 pod ip 摘掉」。
那上面说的设置 ipvs rs weight 来停止新连接的转发,在 kube-router 中有没有实现呢?我们在阅读源码时,发现下面这一部分代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| // Run periodically sync ipvs configuration to reflect desired state of services and endpoints
func (nsc *NetworkServicesController) Run(healthChan chan<- *healthcheck.ControllerHeartbeat, stopCh <-chan struct{}, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
......
// loop forever until notified to stop on stopCh
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
nsc.mu.Lock()
nsc.readyForUpdates = false
nsc.mu.Unlock()
glog.Info("Shutting down network services controller")
return
case <-gracefulTicker.C:
if nsc.readyForUpdates && nsc.gracefulTermination {
glog.V(3).Info("Performing periodic graceful destination cleanup")
nsc.gracefulSync()
}
......
}
|
NSC 中存在一个 graceful 定时器,触发时会执行 nsc.gracefulSync 函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| // proxy/network_service_graceful.go
func (nsc *NetworkServicesController) gracefulSync() {
nsc.gracefulQueue.mu.Lock()
defer nsc.gracefulQueue.mu.Unlock()
var newQueue []gracefulRequest
// Itterate over our queued destination removals one by one, and don't add them back to the queue if they were processed
for _, job := range nsc.gracefulQueue.queue {
if removed := nsc.gracefulDeleteIpvsDestination(job); removed {
continue
}
newQueue = append(newQueue, job)
}
nsc.gracefulQueue.queue = newQueue
}
func (nsc *NetworkServicesController) gracefulDeleteIpvsDestination(req gracefulRequest) bool {
var deleteDestination bool
// Get active and inactive connections for the destination
aConn, iConn, err := nsc.getIpvsDestinationConnStats(req.ipvsSvc, req.ipvsDst)
if err != nil {
glog.V(1).Infof("Could not get connection stats for destination: %s", err.Error())
} else {
// Do we have active or inactive connections to this destination
// if we don't, proceed and delete the destination ahead of graceful period
if aConn == 0 && iConn == 0 {
deleteDestination = true
}
}
// Check if our destinations graceful termination period has passed
if time.Since(req.deletionTime) > req.gracefulTerminationPeriod {
deleteDestination = true
}
//Destination has has one or more conditions for deletion
if deleteDestination {
glog.V(2).Infof("Deleting IPVS destination: %s", ipvsDestinationString(req.ipvsDst))
if err := nsc.ln.ipvsDelDestination(req.ipvsSvc, req.ipvsDst); err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Failed to delete IPVS destination: %s, %s", ipvsDestinationString(req.ipvsDst), err.Error())
}
}
return deleteDestination
}
|
nsc.gracefulSync 函数主要逻辑是对 ipvs 中 RS 进行删除,判断逻辑如下:
- InActConn 和 ActConn 都为0,则说明没有连接存在,可以直接删除;
- 如果 InActConn 或 ActConn 不为零,但是 pod 删除等待时长已经超过 pod.gracefulTerminationPeriod,则可以直接删除;
- 否则,等待下一次进行;
那 nsc.gracefulQueue 队列是在哪里写入的呢?我们之间检索 gracefulQueue 字段,发现在函数 nsc.ipvsDeleteDestination 中写入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| // proxy/network_service_graceful.go
func (nsc *NetworkServicesController) ipvsDeleteDestination(svc *ipvs.Service, dst *ipvs.Destination) error {
// If we have enabled graceful termination set the weight of the destination to 0
// then add it to the queue for graceful termination
if nsc.gracefulTermination {
req := gracefulRequest{
ipvsSvc: svc,
ipvsDst: dst,
deletionTime: time.Now(),
}
dst.Weight = 0
err := nsc.ln.ipvsUpdateDestination(svc, dst)
if err != nil {
return err
}
nsc.addToGracefulQueue(&req)
} else {
err := nsc.ln.ipvsDelDestination(svc, dst)
if err != nil {
return err
}
}
// flush conntrack when Destination for a UDP service changes
if svc.Protocol == syscall.IPPROTO_UDP {
if err := nsc.flushConntrackUDP(svc); err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Failed to flush conntrack: %s", err.Error())
}
}
return nil
}
|
nsc.ipvsDeleteDestination 判断 nsc.gracefulTermination 如果开启,则不会立即删除。而是,执行下面操作:
- 更新 ipvs 配置,设置 RS weight=0;
- 加入 gracefulQueue 队列中,等待删除;
综上,可以看出 nsc.gracefulTermination 就是开启 ipvs 优雅下线的开关,而这个是通过参数 –ipvs-graceful-termination 来控制的。然后,我们开启 ipvs-graceful-termination 进行测试。
我们对测试应用 http-server 增加优雅下线逻辑:
- 捕获 SIGTERM 信号;
- 捕获到 SIGTERM 信号后,在 http header 中增加 connection: close,也就是在容器下线阶段使用短连接;
然后再进行压测:
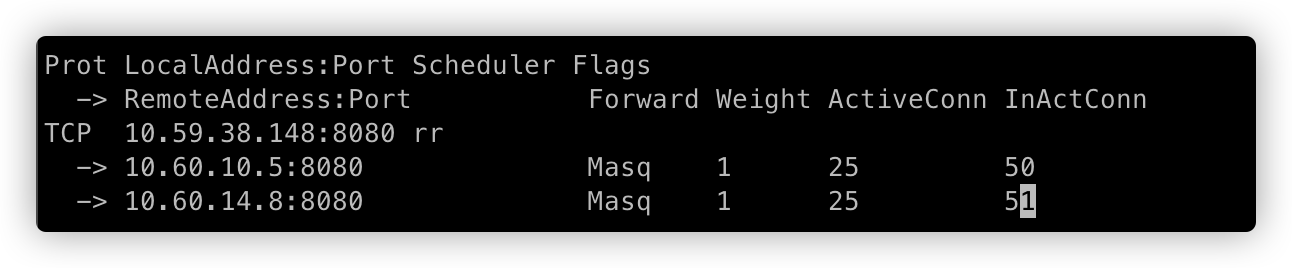 =>
=>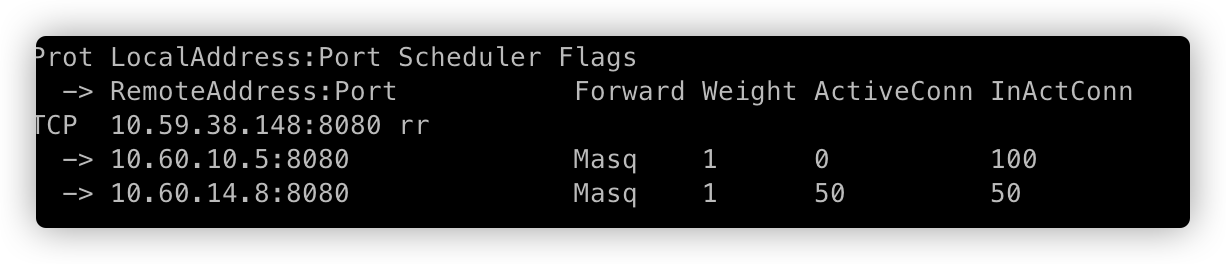 =>
=>
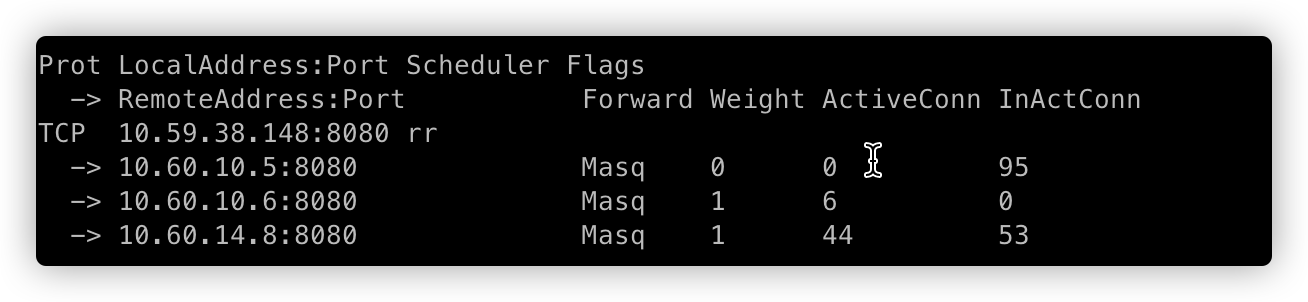 =>
=>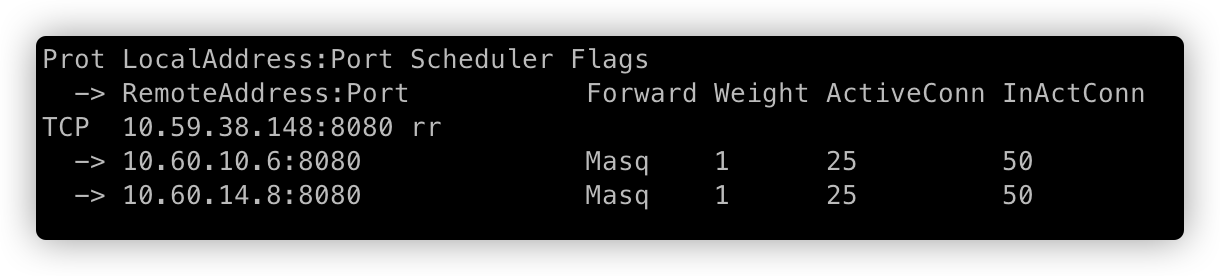
上面分别对应,销毁 Pod 前、销毁 Pod 过程中1、销毁 Pod 过程中2、Pod 被完全销毁。
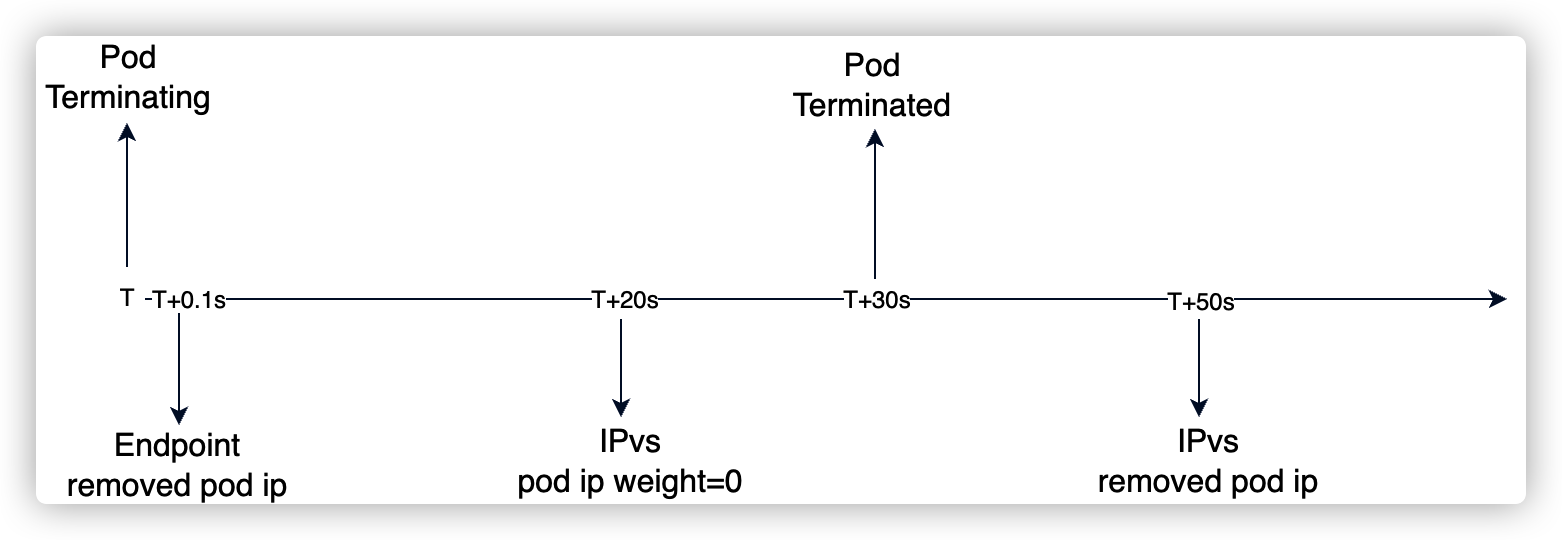
通过开启 ipvs graceful terminated,并且容器销毁后应用捕获 SIGTERM 信号进行连接的优雅下线,测试中未出现请求错误的问题。
总结
对以上源码研究,进行总结如下:
- kube-router 每次更新都是全量更新,service 数量不同 ipvs RS 新增、更新、删除的延迟不同;
- 具有优雅删除 RS 的能力,并且结合了 Pod terminatedGracefulPeriod 进行 RS 的完全删除;
- 为开启 –ipvs-graceful-termination,会立即删除 RS,但是由于全量更新的延迟,表现上是有一定延迟(线下 30s+、线上15s+);
kube-proxy 实现逻辑
根据 1.22 版本 kube-proxy 代码,pod 删除过程:
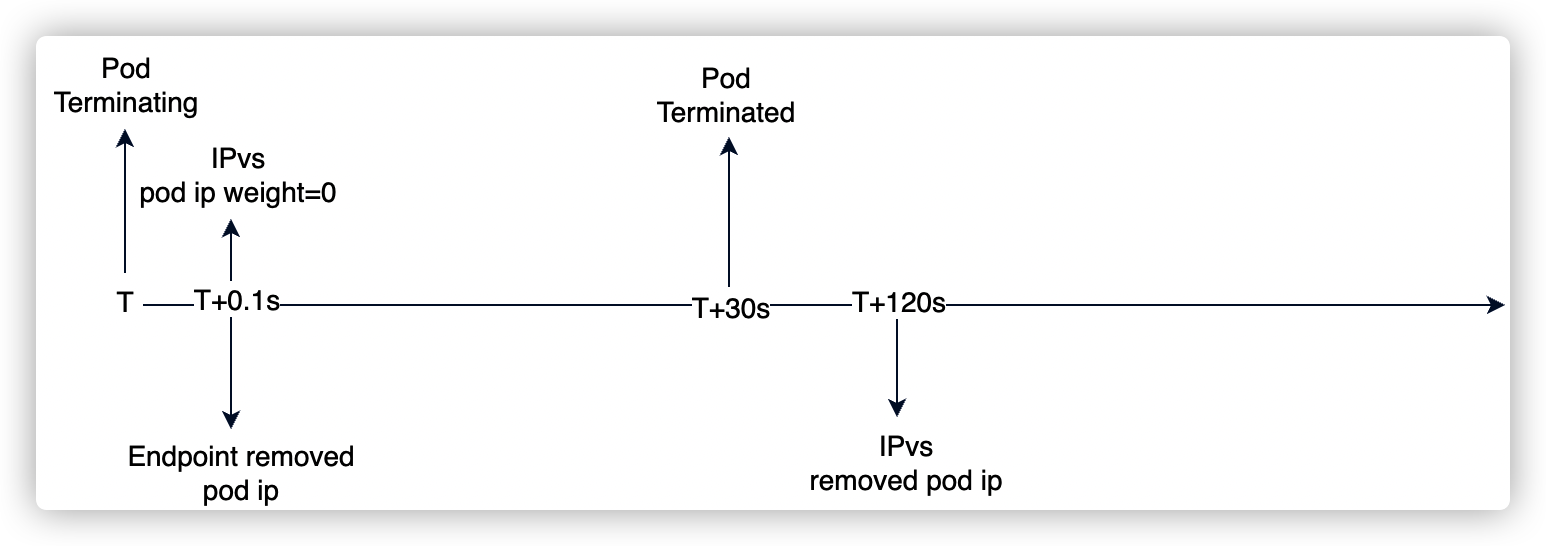
- 销毁 Pod,Endpoint 中移除销毁中的 Pod IP;
- kube-proxy watch 到 endpoint 发生变化,进入 ipvs 删除判断逻辑:
- 协议不是 UDP 或 SFTP;
- ActConn 和 InActConn 都为0;
- 不满足删除判断,则更新 ipvs 中 RS weight=0;
- 然后,将 RS 加入到本地队列,每隔 1min 进行删除判断;
源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| // proxy/ipvs/graceful_termination.go
// GracefulDeleteRS to update rs weight to 0, and add rs to graceful terminate list
func (m *GracefulTerminationManager) GracefulDeleteRS(vs *utilipvs.VirtualServer, rs *utilipvs.RealServer) error {
// Try to delete rs before add it to graceful delete list
ele := &listItem{
VirtualServer: vs,
RealServer: rs,
}
deleted, err := m.deleteRsFunc(ele)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Delete rs %q err: %v", ele.String(), err)
}
if deleted {
return nil
}
rs.Weight = 0
err = m.ipvs.UpdateRealServer(vs, rs)
if err != nil {
return err
}
klog.V(5).Infof("Adding an element to graceful delete rsList: %+v", ele)
m.rsList.add(ele)
return nil
}
func (m *GracefulTerminationManager) deleteRsFunc(rsToDelete *listItem) (bool, error) {
klog.V(5).Infof("Trying to delete rs: %s", rsToDelete.String())
rss, err := m.ipvs.GetRealServers(rsToDelete.VirtualServer)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
for _, rs := range rss {
if rsToDelete.RealServer.Equal(rs) {
// For UDP and SCTP traffic, no graceful termination, we immediately delete the RS
// (existing connections will be deleted on the next packet because sysctlExpireNoDestConn=1)
// For other protocols, don't delete until all connections have expired)
if utilipvs.IsRsGracefulTerminationNeeded(rsToDelete.VirtualServer.Protocol) && rs.ActiveConn+rs.InactiveConn != 0 {
klog.V(5).Infof("Not deleting, RS %v: %v ActiveConn, %v InactiveConn", rsToDelete.String(), rs.ActiveConn, rs.InactiveConn)
return false, nil
}
klog.V(5).Infof("Deleting rs: %s", rsToDelete.String())
err := m.ipvs.DeleteRealServer(rsToDelete.VirtualServer, rs)
if err != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("Delete destination %q err: %v", rs.String(), err)
}
return true, nil
}
}
return true, fmt.Errorf("Failed to delete rs %q, can't find the real server", rsToDelete.String())
}
|
kube-proxy GracefulDeleteRS 函数会 deleteRsFunc 进行 RS 删除,删除 RS 条件:
- 协议不是 UDP 或 SFTP;
- ActConn 和 InActConn 都为0;
否则,更新 ipvs 将 RS weight 置为 0,不接收新流量进入。然后会加入到带删除列表中,进行定期(间隔1min)清理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| func (m *GracefulTerminationManager) tryDeleteRs() {
if !m.rsList.flushList(m.deleteRsFunc) {
klog.Errorf("Try flush graceful termination list err")
}
}
// Run start a goroutine to try to delete rs in the graceful delete rsList with an interval 1 minute
func (m *GracefulTerminationManager) Run() {
go wait.Until(m.tryDeleteRs, rsCheckDeleteInterval, wait.NeverStop)
}
|
优化方案
| | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|
| 方案一 | kube-router 开启 –ipvs-graceful-termination 参数 | | |
| 方案二 | 开发内网负载均衡组件 | | |
参考
- http://www.dockone.io/article/9441
- https://wsgzao.github.io/post/lvs-nat/
- Issue 572 - Graceful termination
- kube-proxy ipvs support graceful termination





 ==》
==》

 =>
=> =>
=> =>
=>


